After-tax income is a crucial financial concept that plays a significant role in personal and business financial planning.
It represents the amount of money an individual or entity has left after deducting taxes from their gross income.
Understanding after-tax income helps in budgeting, savings, and investment decisions.

What Is After-Tax Income?
After-tax income refers to the net earnings received after subtracting taxes such as federal, state, and local taxes from gross income.
This figure represents the actual disposable income available for spending, saving, or investing.
For instance, if you earn a salary of $60,000 annually and your total tax liability is $12,000, your after-tax income would be $48,000.
This amount is what you can use to cover living expenses and achieve financial goals.
Why Is After-Tax Income Important?
1. Helps in Budgeting
Knowing your after-tax income enables you to create a realistic budget. Since this is the amount you can actually spend, planning your expenses based on after-tax income prevents overspending and ensures financial stability.
2. Guides Investment Decisions
When evaluating investment opportunities, after-tax income helps assess the affordability and potential impact on disposable income.
For example, investing in a tax-deferred retirement account might increase your after-tax income over time.
3. Determines Loan Eligibility
Lenders often consider your after-tax income to evaluate your ability to repay loans.
A clear understanding of this metric can help you plan loan applications more effectively.
How to Calculate After-Tax Income
Calculating after-tax income involves three steps:
Start with Gross Income: This includes salary, bonuses, and any additional earnings.
Deduct Taxes: Subtract federal, state, and local taxes. If applicable, include other withholdings such as Social Security and Medicare.
Result: The remainder is your after-tax income.
Example Calculation:
Suppose an individual earns $5,000 monthly.
If federal taxes amount to $750, state taxes are $250, and Social Security and Medicare deductions total $375, the after-tax income is:
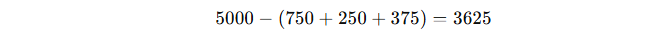
Thus, the monthly after-tax income is $3,625.
Factors Affecting After-Tax Income
Several factors influence after-tax income, including:
Tax Brackets: Higher earners may fall into higher tax brackets, reducing their after-tax income.
Deductions and Credits: Utilizing tax deductions (e.g., mortgage interest) or credits (e.g., child tax credit) can increase after-tax income.
Location: State and local tax rates vary, impacting the amount of disposable income.
Real-World Applications of After-Tax Income
1. Retirement Planning
Retirees often consider after-tax income when withdrawing from retirement accounts.
For instance, withdrawals from a traditional 401(k) are taxable, while Roth IRA withdrawals are typically tax-free, affecting after-tax income differently.
2. Employment Offers
When comparing job offers, after-tax income provides a clearer picture of take-home pay than gross salary.
This allows for better decision-making regarding employment opportunities.
Final Thoughts
Understanding after-tax income is essential for effective financial management.
It helps individuals and businesses make informed decisions about spending, saving, and investing.
By calculating and analyzing this metric, you can better align your financial strategies with your goals and obligations.
$10 Amazon Gift Card Giveaway #017
Explore all 23 giveaways by visiting our Giveaways Main Page
$10 Amazon Gift Card Giveaway #017Disclaimer: The information provided on this website is intended for educational and entertainment purposes only. It should not be considered as professional advice or a substitute for consultation with a qualified professional. Always seek the guidance of a licensed expert in the relevant field for advice tailored to your specific circumstances. The creators of this site assume no responsibility for how the information is used or interpreted.
Quick Links: You can visit financial literacy terms beginning with letters A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X, Y, Z, NUMERICAL, and Glossary